Private Cloud Storage Explained: Benefits and Use Cases
- ellenmalfliet2
- 10 sep
- 10 minuten om te lezen
Before, the question of where data was located would often be an afterthought. Today, it is at the forefront of every compliance audit, procurement checklist, and contract negotiation, especially for companies doing business in or with the European public sector.
So how did we get here, and more importantly, what does it mean for your business?
This shift has become an existential crisis of digital sovereignty. Modern enterprises are caught between the convenience of public cloud offerings and the harsh reality of increasingly strict data governance requirements. One data breach, one failed audit, or one cross-border policy change can undo years of progress and damage carefully built trust.
This comprehensive guide slices through the uncertainty to deliver everything you need to know about private cloud storage.
What is Private Cloud Storage?
Consider the private cloud storage as sharing a digital version of your own safe, rather than leasing an available storage area in a shared storage facility. Unlike public clouds, where data is stored (along with the data of thousands of other companies), private cloud storage offers exclusive access to computing resources, storage, and infrastructure.
At the basic level, the private cloud storage is based upon three simple principles:
Single-tenant environment
Customizable infrastructure
Controlled access
Quick Comparison Table

Types of Private Cloud Storage
All private clouds are not created equal. Familiarity with the different deployment models enables you to choose the approach that is most suitable for your company's security requirements, technical competency, and cost constraints. Below are the five main types of private cloud storage with unique strengths for distinct business scenarios.

1. On-Premises Private Cloud
On-premises private cloud is the most traditional approach, where your organization owns and operates each infrastructure component within your data center. You purchase servers, storage arrays, and networking equipment, install them in your data center, and are responsible for maintaining them.
When to Use: Very highly regulated industries like defense contractors, financial institutions handling trading algorithms, or healthcare companies handling patient information. Also most suitable when you need maximum customization or have special hardware requirements that standard providers are not capable of doing.
2. Hosted Private Cloud
Hosted private cloud strikes a balance between control and convenience by leveraging third-party data centers while maintaining dedicated resources exclusively for your organization.
The Nomadesk Model
It provides you with a flexible option whereby you are liberated with your own private cloud system. As opposed to shared hosting, you may adopt the infrastructure on your own or may have it supported in a secure data center of your preference. That is the best of both worlds: it makes use of cloud computing with full control to physically locate data.
Key Benefits:
Single-purpose infrastructure: No sharing with other organizations
Complete data and location control: Only on-premises or data centers you trust
Security on enterprise level: containerized architecture, uniform deployment, and performance
EU data sovereignty: data centers located in Frankfurt and Amsterdam for EU mandates
Choice of expert deployment: Deploy in minutes or employ expert services
Packed with all features to enable secure file sharing, wide access, real-time collaboration, and enterprise security
Nomadesk Private solution illustrates how the data sovereignty issue can be met through a hosted private cloud. The product fits the compliance needs and provides a privacy-sophisticated, high-availability option as an alternative to a well-populated public cloud with all collaboration capabilities.
3. Managed Private Cloud
Managed private cloud takes it a step further than the hosted model by outsourcing not just the infrastructure, but also the day-to-day management of your private cloud infrastructure.
It encompasses:
Management and server provisioning
Monitoring and updates in security
Backup and recovery management
Performance optimization
Scaling and capacity planning
Ideal For:
Companies that do not have IT experience internally
Fast-growing companies
Firms that desire to concentrate on the root operations
Teams that require rapid scaling without recruiting experts
4. Virtual Private Cloud (VPC)
Virtual Private Cloud constructs a segregated, private zone in a public cloud provider infrastructure using software-defined network and security controls.
How It Works: Your resources are logically separated from other customers using:
Virtualization technology
Advanced firewalls
Network segmentation
Customized security policy
5. Community Private Cloud
Community private cloud hosts several organizations sharing similar compliance, security, or operational needs on a communal private infrastructure.
Shared Benefits: It is a members-only club for organizations with similar needs; costs are split among numerous customers, with increased security and control levels compared to the public cloud.
Key Benefits of Private Cloud Storage
The advantages of private cloud storage go beyond basic security protocols. These five inherent advantages uncover the reasons businesses are deciding to go with private cloud solutions to meet their business and compliance requirements, which are continually evolving.
1. Enhanced Security & Compliance
Private cloud storage provides unmatched security control, and thus it's the first choice for organizations handling sensitive data or operating in extremely regulated markets.
Data Sovereignty Control
The control over the location of your data is fully possible through a private cloud. The idea that Nomadesk wants to use the European data centers located in Frankfurt and Amsterdam is an excellent instance of the given principle, as the sensitive European business data would never leave the EU jurisdiction.
Key Compliance Benefits:
GDPR compliance easily tackled through EU-based hosting
Tailor-made security routines that meet your industry requirements
End-to-end audit trails with complete openness for compliance specialists
Regulatory needs like HIPAA, SOX implemented effortlessly
2. Complete Control & Customization
The private cloud avoids the one size fits of the public cloud candidates.
What You Have Control of:
Possibility of configuring both hardware and software choices
Design of the system according to your requirements
Access controls following organizational organization
Classification of data and authorisation of workflows
3. Superior Performance
Dedicated infrastructure resources translate exactly into consistent, high-performance computing and storage capacity.

Performance Advantages:
No competition on bundled CPU, memory, and storage devices
Foreseeable metrics play a major role in SLA needs
Personalized network configuration that is streamlined to your traffic
Improved low-latency due to strategic placement of servers
4. Cost Predictability (Long-term)
Although a private cloud will be capital-intensive in the short run, it proves to be very cost-effective on a long-term basis and also on constant storage requirements.
Financial Advantages:
No surprise bills due to usage spikes or data transfer fees
Fixed, predictable expenses that align with budgeting cycles
Better ROI on large-scale deployments (typically breaks even in 2-3 years)
Fewer vendor lock-in risks and contract flexibility
5. Business Continuity
Private cloud infrastructure provides greater control over business continuity planning and disaster recovery.
Flexibility Advantage: Private cloud provides you with options when your needs vary. You can start with a hosted private cloud solution and move up to completely on-premises infrastructure, or vice versa. You can even have some data in a private cloud and use public cloud for less sensitive work, without having to rewrite your systems or retrain your people.
Real-World Use Cases
According to a Flexera 2024 survey, in the contemporary environment, 87% of companies are deploying their infrastructure in private clouds today, owing to the popularity of compliant markets that encourage the adoption to meet their compliance and security demands. The following are some of the examples of how the various industries are using private cloud storage as a solution to their individual needs.
1. Financial Services
Financial institutions are governed by some of the most stringent data protection laws in any industry, so private cloud storage is an integral component of their technology plan.
Regulatory Requirements
Financial institutions and banks must comply with regulatory standards like SOX, PCI DSS, and Basel III, which require detailed audit trails, encryption of data, and access controls that are mandatory. Private cloud infrastructure allows organizations to implement tailored compliance models that meet a variety of regulatory requirements simultaneously.
Which Private Cloud Type Works Best
The majority of the financial organizations utilize on-premises private cloud for their most confidential customer and trading data, while hosted private cloud is kept for less important applications like employee collaboration tools and document management. It adopts a blend of maximum security and operational effectiveness.
2. Healthcare Organizations
Medical workers deal with personal data, which needs to be well-protected and easily integrated with other systems.
Why Private Cloud Works: Patient-specific access controls may be implemented by healthcare organizations, and complete audit trails for all data interaction may be maintained, yet they are able to natively integrate the specialty medical software having particular network requirements.
3. Government & Public Sector
The security demands of government agencies are rather specific, which can be easily solved by using private cloud storage.
Key Considerations:
Data Sovereignty: The EU government contracts state that data has to stay within the European borders
Security Clearances: Background-cleared workforce and separated networks
Procurement Compliance: Special certifications and compliance rules of vendors
Classic Deployment: Standardized combination of public sector agency shared private cloud, suitable security requirements, and therefore reduced costs. This would, however, be in very high compliance standards.
4. Manufacturing & Industrial
Manufacturing companies need robust data protection for competitiveness and operational efficiency.
Protection Priorities:
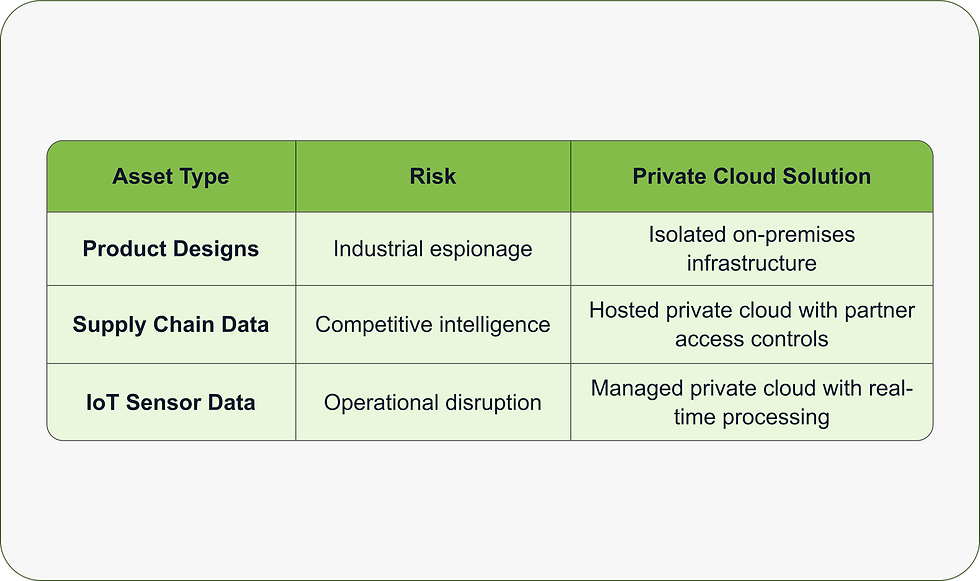
Advantages of Integration: The private cloud can process the huge amount of IoT sensor data, and it will be connected to current manufacturing execution systems to enable real-time monitoring of the data without exposing confidential information.
5. Legal & Professional Services
The law firms deal with some sensitive information of their clients, which needs maximum security and privacy.
Recommended Configuration: Most law firms are adequately served by a hosted private cloud with EU data centers to support EU clients and standalone infrastructure for the remainder of the world to meet region-specific governance models.
These industries do not go private cloud for convenience; they do so because their business models, regulatory frameworks, and competitive standing are built on having total control of their data infrastructure.
Private Cloud Storage Providers
Not all the providers of the private cloud respond to these problems in the same way. They include technical capability-driven and compliance and data-driven. Knowing the strengths and weaknesses of a single vendor would help you in locating the correct solution to support your business requirements and rules.

1. Nomadesk
European Data Sovereignty Leadership
Nomadesk was designed upon the premise that the location of data now is at the center of any audited dealing with compliance, purchase, and contract discussions. They begin with the aspect of European data sovereignty, where the services of the public clouds will be placed only at the European data centers that achieve the best European levels of security and privacy.
Core Advantage:
Teams can "travel between public and private infrastructure as required, without disruption or reconfiguration." It's an unparalleled value for companies working with sensitive data under region-specific governance paradigms, where there is total location ownership and access without the typical migration headaches.
Why Nomadesk:
European-first strategy: Designed with GDPR and EU compliance from the ground up
Seamless deployment: Flexible across public and private infrastructure
Zero-disruption: Transitions with evolving business needs
Data protection: Expertise in European regulations
Streamlined compliance: Through a specially developed European infrastructure
2. IBM Cloud
Enterprise-Level Private Cloud Solutions
IBM Cloud offers a fully featured private cloud infrastructure with advanced enterprise-class features, extensive security certifications, and integration support for big deployments.
Comparison Point:
While IBM does have good enterprise features, its deployment model isn't nearly as flexible as Nomadesk's. Businesses usually go through complex migrations and lengthy reconfigurations when switching between deployment models.
Limitation:
IBM's global approach equals less concentrated expertise on European compliance requirements than vendors built from the beginning for EU data sovereignty requirements. Their solutions require more configuration to accommodate regional governance structures.
3. Microsoft Azure
Azure Stack for Hybrid/Private DeploymentsMicrosoft Azure Stack extends Azure services to on-premises, providing a hybrid cloud using the same Azure tools and interfaces.
Broad Compliance CertificationsAzure supports numerous compliance certifications in a number of different industries and geographies, thereby enabling organizations with diverse regulatory requirements.
Compliance requirements:The opposite of Nomadesk's approach with an open mind about deployment flexibility is related to Azure vendor lock-in issues. Companies that invested heavily in Azure services might not manage to relocate to other solutions under such circumstances.
4. Amazon Web Services (AWS)
AWS Outposts for On-Premises Private CloudAWS Outposts brings AWS services natively into on-premises data centers, allowing organizations to host AWS infrastructure in their own data centers.
Mature Ecosystem and ToolsAWS offers the widest pool of cloud services and third-party integration, with a gigantic set of options for deploying and developing applications.
Data Residency Issues:As a US-headquartered company, AWS is always facing pressure about data sovereignty for European enterprises. Their complex pricing models also contrast with more transparent European-focused alternatives offering deterministic compliance-driven solutions.
5. Google Cloud
Anthos for Hybrid and Multi-CloudGoogle Cloud Anthos platform enables on-prem deployment of apps, on Google Cloud, and in other cloud environments by using a Kubernetes-based architecture.
Sophisticated AI/ML CapabilitiesGoogle Cloud delivers leading artificial intelligence and machine learning services, which attract sophisticated analytics-requiring organizations.
Limitation:Privacy concerns and data management policies restrain European organizations, especially in comparison with privacy-first European compliance-centric providers such as Nomadesk.
Provider Comparison
Common Challenges & Solutions
Typical Obstacles
Initial Setup Difficulty
Most organizations fear that private cloud deployment involves a lot of technical planning, difficult infrastructure choices, and protracted implementation cycles. The misconception that private cloud equates to "doing everything yourself" generates undue pause among executives.
Higher Upfront Charges
The high cost of investing in the infrastructure of a private cloud can be perceived to be enormous when compared to the small amounts invested in public clouds. Budget planners encounter capital costs models by people who are used to operating expense models.
Skills Needed
Private cloud management seems to necessitate technical expertise that is lacking in most organizations' internal workforce. The seeming necessity of dedicated cloud architects and security specialists creates personnel and training problems that render serious consideration of private cloud options unrealistic.
How to Overcome Them
Managed Services ApproachExisting private cloud providers realize that firms need solutions, not further complexity. Nomadesk's approach is a classic example of such understanding; their solution may be "deployed directly into private infrastructure" with professional management, or firms can "deploy it yourself within minutes," depending on internal resources.
Key Benefits:
No-cost operating work without loss of data authorship
Professional handling of infrastructure without the need for staff
Adaptable capabilities that resemble organizational capabilities
The complexity problem is not with the technology itself, but with getting the right partnership model that gives business outcomes without overwhelming internal resources.
Conclusion & Next Steps
Private cloud storage has grown from being a specialist solution to being a fundamental approach for companies committed to data control and compliance. The issue isn't whether you require greater control; it's whether your existing infrastructure can keep up with dynamically shifting regulatory demands.
Take Action
Check your compliance confidence
Determine your data sovereignty needs
Review providers with deployment flexibility
Want European data sovereignty or easy deployment choices? Nomadesk's double-deployment solution addresses specific compliance challenges and provides flexibility to grow with your business.
Ready to find solutions that suit your requirements?
Try Nomadesk’s free trial today to find out how our private cloud solutions can provide the control over your data and compliance guarantee your business requires.



Opmerkingen